Table of Contents
Fixed vs Flexible Energy Contracts: What is the difference?
Many people are wondering what is the best approach: a fixed or flexible energy contract?
A fixed energy contract is the more traditional way to procure energy. Fixed energy contracts are agreements between an energy buyer and supplier, where the energy price is set at a specific amount and remains fixed for the duration of the contract. The agreed energy price remains fixed for the duration of the contract. These contracts provide price stability and predictability of energy costs, making it easier for the energy buyer to budget future energy costs. However, they also expose the buyer to the risk of declining energy market prices in the energy market, as the fixed price may become uncompetitive over time.
A flexible energy contract, on the other hand, allows the adjustment of energy prices based on changes in the market or other relevant factors. This type of contract is fit for more experienced energy buyers. Wholesale energy is purchased in several tranches throughout the length of the contracts.
These contracts are more dynamic and allow the energy buyer to take advantage of market conditions, but they also come with increased price risk compared to fixed contracts. Flexible energy contracts are normally available to larger customers with a consumption of 8 GWh/year and above. They allow for spreading the risk of purchasing decisions throughout the year. In such a way, you don’t “put all your eggs in one basket”. Flexible energy contracts can take different forms, such as indexed contracts, formula-based contracts, or contracts that allow for adjustment of the energy price based on specific events or conditions.
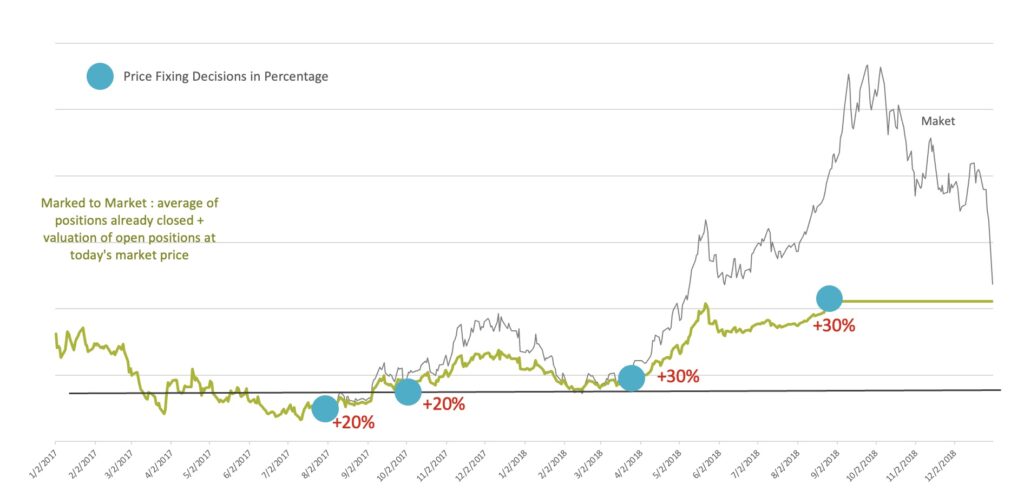
In a flexible contract, you set up a framework agreement with a supplier (setting up payment terms, invoicing, liabilities, etc) for a period of time and buy when you believe it is advantageous. The process, however, can be complex and depends on having up-to-date market information available to help you decide when the purchasing decisions should be made. You would also usually need to develop a robust risk management strategy to manage the market price risk.
The choice between fixed and flexible energy contracts depends on the energy buyer’s specific needs and risk tolerance. Fixed contracts provide price stability and predictability, while flexible contracts offer greater price flexibility and the ability to respond to changes in the energy market dynamics. In recent times, however, more and more corporate buyers prefer to switch to flexible energy procurement strategies to take advantage of the rapidly changing market dynamics as well as to be able to incorporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) into their flexible power supply.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fixed Energy Contracts
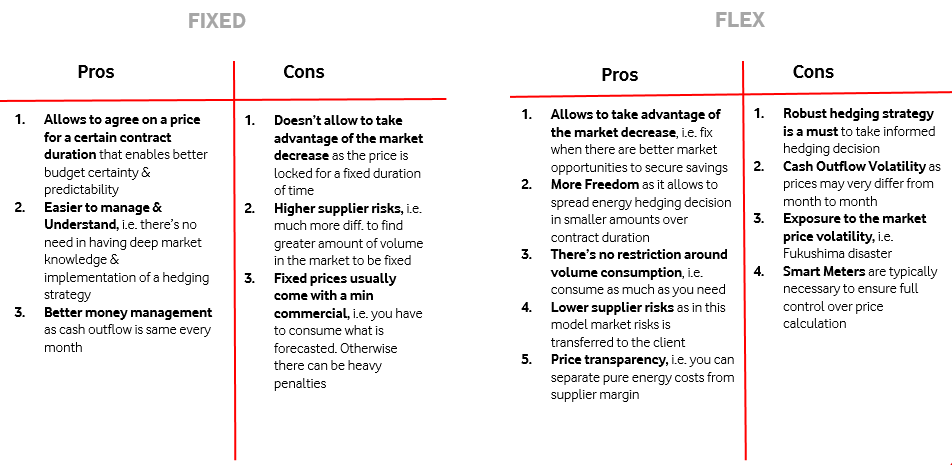
Fixed energy contracts are agreements between energy buyers and suppliers, where the price of energy is set at a specific time and remains fixed for the duration of the contract. The fixed energy contract duration typically ranges from 1 to 3 years. These contracts have both advantages and disadvantages, which are discussed below.
Advantages of fixed energy contracts:
- Price stability: Fixed energy contracts provide price stability, allowing energy buyers to budget and plan effectively. This helps them to avoid unexpected energy costs and to make long-term investment decisions with greater confidence.
- Predictable energy costs: Fixed energy contracts allow energy buyers to know exactly what they will be paying for energy, making it easier to forecast their energy costs and manage their budgets.
- Simplified procurement process: Fixed energy contracts simplify the procurement process, as the energy price is set and agreed upon at the start of the contract. This reduces the need for ongoing negotiations and can save time and resources for both the energy buyer and supplier.
Disadvantages of fixed energy contracts:
- Price Risk: Fixed energy contracts expose energy buyers to the risk of price changes in the energy market. If the fixed price becomes uncompetitive, the energy buyer may be paying more for energy than the market rate. Once signed, fixed energy contracts become a financial commitment for the buyer to offtake electricity at the agreed fixed energy rate.
- Lack of flexibility: Fixed energy contracts often lack flexibility, as the energy price cannot be adjusted based on changes in the market or other relevant factors. If the market prices decline, this may result in energy buyers missing out on opportunities to save money or to source energy from more cost-effective sources.
- Risk of over- or under-procurement: Fixed energy contracts may lead to over- or under-procurement of energy, as the energy buyer may not be able to adjust their energy usage based on changes in demand or availability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible Energy Contracts
These contracts offer greater price flexibility compared to fixed contracts but also come with increased price risk. The following are some of the advantages and disadvantages of flexible energy contracts.
Advantages of flexible energy contracts:
- Price flexibility: Flexible energy contracts allow energy buyers to respond to changes in the energy market, which can help them save money and source energy more cost-effectively.
- Protection against price volatility: Flexible energy contracts provide protection against price volatility, as the energy price can be adjusted based on changes in the market. This can help energy buyers to manage their energy costs more effectively and to avoid paying too much for energy.
- Increased energy security: Flexible energy contracts can increase energy security, as they allow energy buyers to adjust their energy usage based on changes in demand or availability. This can help to ensure that energy buyers have access to the energy they need when they need it.
Disadvantages of flexible energy contracts:
- Increased price risk: Flexible energy contracts expose energy buyers to increased price risk, as the energy price can fluctuate based on changes in the market. This may result in energy buyers paying more for energy than they would under a fixed contract.
- More complex procurement process: Flexible energy contracts may be more complex than fixed contracts, as they often involve ongoing negotiations and adjustments to the energy price. This can make the procurement process more time-consuming and resource-intensive for both the energy buyer and supplier.
- Less predictable energy costs: Flexible energy contracts can make it more difficult for energy buyers to predict their energy costs, as the energy price can fluctuate over time. This can make it harder for energy buyers to budget and plan effectively.
While flexible contracts allow energy buyers to respond to changes in the market and protect against price volatility, they also expose the energy buyer to increased price risk and may result in more complex procurement processes. On the other hand, in the low commodity market price environment, a fixed-price energy contract can be very appealing as it would protect organizations against rising costs in the future, especially as we know commodity markets are cyclical.
Therefore, a fixed energy contract is more suitable for businesses that are more risk-averse and requires stability and budget certainty over a period.
In conclusion, the choice between a fixed price or variable price energy contract will depend on your energy needs and risk tolerance. If you need stability and predictability, a fixed price contract may be the best choice, while a variable price contract may be more suitable if you are willing to take on the added risk of fluctuating energy prices.
Why would a business choose to continue buying energy using a fixed strategy?
A business might choose to continue buying energy using a fixed strategy for several reasons, including:
- Budget stability: Fixed energy contracts provide a set price per unit of energy, which can help businesses budget and plan their energy expenses more accurately.
- Predictability: With a fixed energy contract, businesses can anticipate their energy costs and plan their budgets accordingly.
- Reduced risk: Fixed energy contracts can reduce the risk of volatile energy prices, which can significantly impact a business’s bottom line.
- Simplicity: Fixed energy contracts are typically straightforward and easy to understand, making it easier for businesses to manage their energy expenses.
- Long-term planning: Fixed energy contracts can provide a more stable and predictable environment for businesses that require long-term planning, such as manufacturing or data centers.
Fixed or flexible energy contracts: where to start?
The following steps can help energy buyers get started:
- Assess your energy needs: Determine your energy usage patterns, energy needs, and future energy requirements. This will help you understand which type of energy contract best suits your needs.
- Research the market: Conduct thorough research on the energy market to understand current energy prices, trends, and available energy contract options.
- Consider your risk tolerance: Evaluate your risk tolerance and consider whether you are comfortable with the risks associated with a fixed or flexible energy contract.
- Consult with an expert: Consult with an energy specialist or broker to discuss your energy needs and receive advice on the best energy contract option.
- Compare offers: Compare offers from different energy suppliers to determine the best option for your needs. Consider factors such as the energy price, contract length, and flexibility of the contract.
- Review the contract terms: volume tolerance clauses, price adjustment clauses, liabilities and guarantees, pass-through, and other hidden costs should be considered. An energy expert can help you benchmark and value different energy supply proposals and choose the best one for you.
Energy unit price costs breakdown
The unit price of energy is typically comprised of several components, including:
- Generation costs: These are the costs of producing electricity, including fuel, labor, and capital expenditures.
- Transmission and distribution costs: These are the costs of delivering electricity from the generation source to homes and businesses.
- Government taxes and levies: These include taxes, fees, and other charges imposed by the government to fund specific programs or initiatives.
- Retailer margin: This is the profit that the energy retailer makes on the sale of electricity.
- Environmental costs: These are costs associated with reducing the impact of energy production and consumption on the environment, such as renewable energy initiatives and carbon offset programs.
It’s important to compare energy prices from different providers to determine the best option for your needs.
How does flexible energy procurement affect my billing?
Both Flexible and Fixed energy procurement can affect your billing in several ways:
- Billing frequency: Energy bills can be issued monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the contract and the energy provider.
- Billing amount: With a flexible energy contract, your billing amount will vary based on changes in energy prices. When energy prices increase, your bill will likely increase, and vice versa.
- Billing method: Some energy providers offer real-time or historically estimated billing. Real-time energy billing gives you a more accurate reflection of your energy usage and costs.
- Billing accuracy: Energy bills can sometimes contain errors or overcharges. With a flexible energy contract, it is important to review your bills carefully to ensure that they are accurate and that you are being charged the correct amount.
10 things to consider when negotiating a flexible energy supply contract?
When choosing a flexible energy contract, it is important to consider the following tips:
- Consider your energy usage patterns: Review your historical energy usage data to understand your energy needs.
- Market conditions: Consider current market conditions and energy prices when negotiating a flexible energy contract, as these can significantly imp your energy costs.
- Pricing structure: Review the pricing structure of the contract, including any index-linked pricing, to ensure that it meets your needs and budget.
- Billing and payment terms: Consider the billing and payment terms of the contract, including any late payment fees or penalties, to ensure that they are reasonable and meet your needs.
- Compare contract options and rates from different providers: Shop around and compare different contract options and rates from different energy providers to find the best deal.
- Consider the contract length: Consider the length of the contract and any early termination fees when choosing a flexible energy contract. The contract length is flexible energy procurement can usually be longer than a fixed contract. But consider the market liquidity where your business operates.
- Energy price monitoring: Regularly monitor energy prices to make informed decisions about your energy procurement strategy. Some electricity suppliers may offer these services.
- Consider additional services: Some energy providers offer additional services, such as special energy discounts for employees, energy management, energy audits, and demand response programs that can help you reduce energy costs and improve energy efficiency.
- Provider reputation: Consider the reputation and track record of the energy provider to ensure that they are reliable and trustworthy.
- Read the contract: Review the terms and conditions of the contract, including any clauses that may limit your flexibility or increase your risk, to ensure that they are fair and reasonable.
How can Future Energy Go help you?
A well-thought-out procurement strategy can save you time and money in the future. Future Energy Go procurement team specializes in energy markets and can help choose the best contract for your needs. We can design and develop energy procurement policies and hedging strategies tailored to your business needs so you can take full advantage of energy market dynamics while don’t have to waste time trying to figure it all out on your own.
Curious to learn more about PPAs? Our guide offers a concise roadmap to navigate Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). Learn more here.






