Table of Contents
Introduction: Wind Profile PPA
In recent years, corporate PPAs have gained popularity. Large corporations and businesses have shown interest in directly purchasing renewable energy from developers from a specific renewable energy project. These long-term contracts help companies meet sustainability goals and often secure competitive energy costs.
The choice of power purchase agreement (PPA) structure can have a profound impact on business success. There are multiple PPA profile structures available currently in the market. However, in this article, we are going to dive deep into Fixed Wind Profile PPAs and Pay-as-Produced Generation Profiles.
Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) generation profile refers to the pattern or schedule of when and how electricity is generated by a renewable energy project, such as a wind farm or solar plant. These renewable technologies generate electricity, but they don’t do it at a constant rate all the time.

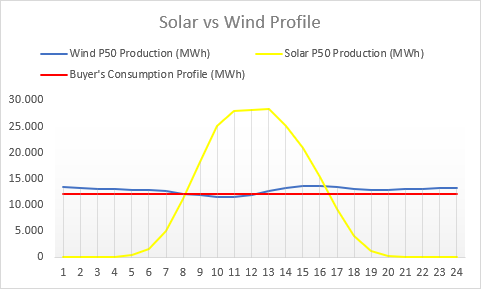
For example, a wind turbine might generate more electricity when the wind is strong, and less when it’s calm. So, its generation profile shows that it produces more electricity during windy periods and less during calm periods. Similarly, a solar panel generates electricity when the sun is shining. So, its generation profile shows that it produces electricity during daylight hours and none at night.
What is profile risk in PPA?
When someone talks about a PPA generation profile, they are interested in understanding what is expected energy generation potential of a specific renewable energy project. This information is important for businesses because it helps them plan the use of renewable electricity.
In this article, we will explore the advantages of Fixed Wind Profile PPAs over Pay-as-Produced Generation Profiles. But first, let’s talk about renewable generation expected volume output.
Renewable Energy Generation: P10, P50 and P90
In the context of renewable energy generation, such as wind or solar power, “P50,” “P90,” and “P10” are statistical terms used to describe different levels of confidence or probability associated with the expected generation from a particular source.

P50 (50th Percentile). P50 represents the median scenario for expected generation. It’s the point at which there’s a 50% chance that the actual generation will be higher than the P50 value and a 50% chance that it will be lower.
P90 (90th Percentile). The lower figure in MWh. P90 represents a more conservative estimate of expected generation. It’s the point at which there’s a 90% chance that the actual generation will be higher than the P90 value and only a 10% chance that it will be lower.
P10 (10th Percentile). The highest figure in MWh. P10 represents an optimistic or best-case estimate of expected generation. It’s the point at which there’s a 10% chance that the actual generation will be higher than the P10 value and a 90% chance that it will be lower.
In conclusion, P90 and P10 come into play when risk mitigation assessment is important. A comprehensive analysis that considers multiple scenarios, including P50, P90, and P10, provides a more holistic perspective on the potential outcomes and risks associated with renewable energy PPAs.
Higher percentiles such as P75 and P90 offer a more conservative view when assessing the economics of Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), particularly for wind projects. These percentiles are particularly valuable for those who prioritize risk mitigation and want to ensure a robust business case.
Understanding the Two PPA Structures
Before diving into the advantages, let’s briefly explain what Fixed Wind Profile PPAs and Pay-as-Produced Generation Profiles are.
Fixed Wind Profile PPA
A Fixed Wind Profile PPA is an agreement where the buyer pays a predetermined fixed price for a predetermined electricity volume generated by a wind energy project over the PPA contract terms. This fixed price and the 24h wind generation profile remain constant over the contract term. This structure is often favored for its stability and predictability by buyers.
Pay-as-Produced PPA Generation Profile
In a Pay-as-Produced or Pay-as-Generated Profile PPAs, the buyer pays for the actual electricity production generated by a renewable Wind or Solar project. The price is often tied to the variable output of the wind turbines or solar radiation meaning it can fluctuate based on the specific project performance. While this structure can offer flexibility, it also introduces electricity supply volume volatility risk.
Wind vs. Solar Renewable Energy Technologies
Wind and solar energy are two prominent forms of renewable energy technologies, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Globally, these technologies have seen significant growth and continue to play crucial roles in the transition to a sustainable energy future.
| Wind Energy | Solar Energy |
| Pros: | Pros: |
| 1. High Energy Potential | 1. Abundant Resource |
| 2. Mature Technology | 2. Modularity, i.e. solar panels can be integrated on both on-site and off-site |
| 3. Scalability | 3. Low Operating Costs |
| 4. Low Environmental Impact | 4. Silent Operation |
| Cons: | Cons: |
| 1. Intermittent Supply | 1. Generates only during sun-light day hours |
| 2. Visual and Noise Impact | 2. Energy Storage Challenges |
| 3. Space Requirements | 3. Space Requirements |
In conclusion, wind energy generation is relatively constant as long as there is sufficient wind to turn the turbines. Unlike solar, which is limited to daylight hours, wind turbines can generate electricity 24/7. This makes wind energy a valuable resource for providing a consistent power supply, especially for businesses that operate 24/7.
However, one of the challenges with wind technology is its unpredictability. Wind patterns can vary significantly from hour to hour, from day to day and from year to year. This unpredictability makes it challenging to forecast the exact amount of electricity that a wind farm will produce at any given time, which can introduce uncertainty for corporate energy buyers.
On the other hand, Solar energy is more predictable in terms of daily and seasonal patterns. This predictability allows energy buyers to plan for the expected output of solar installations with a high degree of accuracy. However, solar generation drops to zero during the night if no storage solutions like batteries are installed. Given these differences in generation profiles, it often makes more sense to fix the generation profile in PPAs for wind energy but not necessarily for solar energy because solar generation is already highly predictable within daylight hours.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Wind Profile PPA and Pay-as-Produced Generation Profile PPA
| Fixed Wind Profile PPA | Pay-as-Produced Generation Profile PPA |
| Pros: | Pros: |
| 1. Volume Supply Predictability, i.e the project developer assumes the risk of underperformance | 1. Volume Generation Flexibility |
| 2. Budget Predictability | 2. Performance-Linked Pricing |
| 3. More Accurate Hedge | 3. Initial Cost Savings, i.e. Pay-as-Produced agreements may offer lower initial energy costs |
| Cons: | Cons: |
| 1. Potentially Higher Initial Costs, i.e. fixed PPA generation profile may come at a premium and depends on supplier capabilities to manager the risk | 1. Imperfect Hedge as generation is often different from a buyer’s consumption |
| 2. Possible disconnect of the guranteed electricity volume supplied from renewable energy certificates (RECs) from the same project | 2. Market Price Exposure, i.e. the buyer assumes the risk of underperformance |
Final Words
Based on the analysis of Fixed Wind Profile PPAs and Pay-as-Produced Generation Profiles, here are some conclusions and recommendations.
1. Choose PPA Structure Carefully:
When selecting a PPA structure, consider the risk tolerance of your organization, market conditions, and financial objectives. Fixed Wind Profile PPAs are better suited for those seeking stability and long-term pricepredictability.
2. Mitigate Risk Appropriately:
If opting for a Fixed Wind Profile PPA, ensure that risk mitigation strategies are in place to address potential underperformance. This may include performance guarantees from the project developer.
3. Diversify PPA Portfolios:
Consider diversifying your PPA portfolio to balance the advantages and disadvantages of different structures. This can help mitigate risk and provide flexibility in managing energy costs.
4. Stay Informed:
Continuously monitor market conditions and regulatory changes that may impact PPA structures. Being proactive in adapting to industry trends can help optimize your energy procurement strategy.
5. Engage Expert Advisors:
Seek the guidance of energy consultants and legal experts with experience in renewable energy PPAs. Their expertise can help you navigate complex negotiations and contracts effectively.
In conclusion, while both Fixed Wind Profile PPAs and Pay-as-Produced Generation Profiles have their merits, the former offers greater stability and predictability for wind energy projects. The choice between the two should align with your organization’s risk tolerance, financial objectives, and the broader market context. By making informed decisions and considering risk mitigation strategies, businesses can optimize their energy cost for long-term success.
I hope this article has shed some light on different wind and solar generation profiles and how they impact Power Purchase Agreements. As the world continues its transition toward sustainable energy sources, understanding these differences becomes increasingly important.
If you have any questions, insights, or personal experiences related to wind or solar energy, we’d love to hear from you! Please leave your comments below and share your thoughts with our community. Thank you!